OGGM Shop#

OGGM needs various data files to run. We rely exclusively on open-access data that can be downloaded automatically for the user. This data needs to be extracted and pre-processed for each individual glacier. To avoid that everyone needs to repeat these steps, we have added a service that we like to call a “shop”, allowing users to define a shopping list of data that they wish to add to their Glacier directories. The data that can be included your glacier directories range from essentials for standard OGGM workflow to other data, like velocity provided as gridded_data for each respective glacier, that might be of interest to you.
This page describes the various products you will find in the shop. Don’t forget to cite the original data sources of the data that you use (all details can be found the glacier directories, but details are also listed throughout the documentation).
Important
Don’t forget to set-up or check your system (First step: system settings for input data) before downloading new data! You’ll need to do this only once per computer.
Pre-processed directories#
The simplest way to run OGGM is to rely on Glacier directories which have been prepared for you by the OGGM developers. Depending on your use case, you can start from various stages in the processing chain, map sizes, and model set-ups.
The directories have been generated with the standard parameters of the respective OGGM version (and a few alternative combinations). If you want to change some of these parameters, you may have to start a run from a lower processing level and re-run the processing tasks. Whether or not this is necessary depends on the stage of the workflow you’d like your computations to diverge from the defaults (this will become clearer as we provide examples workflow below).
To start from a pre-processed state, simply use the
workflow.init_glacier_directories() function with the
prepro_base_url, from_prepro_level and prepro_border keyword arguments
set to the values of your choice. This will fetch the desired directories:
there are more options to these, which we explain in detail below.
If you like to start using the pre-processed directories right away, with out
reading about all the different options and details first, you can go to the
[10 minutes to… a preprocessed directory](https://oggm.org/tutorials/stable/notebooks/10minutes/preprocessed_directories.html)
tutorial.
Processing levels#
New in version 1.6!
In v1.6, Level 4 and Level 5 have changed! The explanations below are valid for OGGM version 1.6.0 and above.
There are six available levels of pre-processing:
Level 0: the lowest level, with directories containing the glacier outlines only.
Level 1: directories now contain the glacier topography data as well.
Level 2: at this stage, the glacier flowlines and their downstream lines are computed and ready to be used.
Level 3: has the baseline climate timeseries (e.g. W5E5, CRU or ERA5) added to the directories. It also contains all necessary pre-processing tasks for a dynamical run, including the mass balance calibration, bed inversion, up to the
tasks.init_present_time_glacier()task. These directories still contain all data that were necessary for the processing. Therefore they are large in size but also the most flexible since the processing chain can be re-run from them.Level 4: includes a historical simulation from the RGI date to the last possible date of the baseline climate file (currently January 1<sup>st</sup> 2020 at 00H for most datasets), stored with the file suffix
_historical. Moreover, some configurations (calledspinup) may include a simulation running a spinup from 1979 to the last possible date of the baseline climate file, stored with the file suffix_spinup_historical. This spinup attempts to conduct a dynamic melt factor calibration and a dynamic spinup matching the RGI area. If this fails, only a dynamic spinup is carried out. If this also fails, a fixed geometry spinup is conducted. To learn more about these different spinup types, check out Dynamic spinup.Level 5: is same as level 4 but with all intermediate output files removed. The strong advantage of level 5 directories is that their size is considerably reduced, at the cost that certain operations (like plotting on maps or re-running the bed inversion algorithm) are not possible anymore.
In practice, most users are going to use level 2, level 3 or level 5 files. To save space on our servers, level 4 data might be unavailable for some experiments (but are easily recovered if needed).
Changes to the version 1.4 directories
In previous versions, level 4 files were the “reduced” directories with intermediate files removed. Level 5 was very similar, but without the dynamic spinup files. In practice, most users won’t really see a change.
Here are some example use cases for glacier directories, and recommendations on which level to pick:
Running OGGM from GCM / RCM data with the default settings: start from level 5
Using OGGM’s flowlines but running your own baseline climate, mass balance or ice thickness inversion models: start at level 2. When using an own module, for instance for the mass balance, one can still decide to use OGGM again further on in the workflow, for instance for the glacier dynamics. This is the workflow used by associated model PyGEM for example.
Run sensitivity experiments for the ice thickness inversion: start at level 3 (with climate data available) and re-run the inversion steps.
Glacier map size: the prepro_border argument#
The size of the local glacier map is given in number of grid points outside the glacier boundaries. The larger the domain, the larger the glacier can become. Here is an example with Hintereisferner in the Alps:
base_url = 'https://cluster.klima.uni-bremen.de/~oggm/gdirs/oggm_v1.6'
base_url += '/L1-L2_files/elev_bands'
f, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(8, 6))
for ax, border in zip(np.array(axs).flatten(), [10, 80, 160, 240]):
gdir = workflow.init_glacier_directories('RGI60-11.00897',
from_prepro_level=1,
prepro_base_url=base_url,
prepro_border=border)
graphics.plot_domain(gdir, ax=ax, title='Border: {}'.format(border),
add_colorbar=False,
lonlat_contours_kwargs={'add_tick_labels':False})
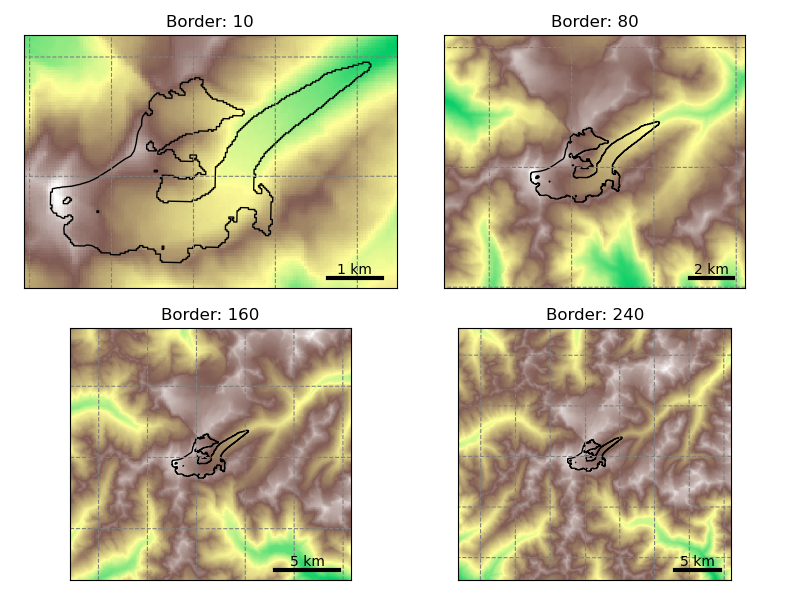
Users should choose the border parameter depending on the expected glacier growth in their simulations. For simulations into the 21<sup>st</sup> century, a border value of 80 is sufficient. For runs including the Little Ice Age, a border value of 160 or 240 is recommended.
Users should be aware that the amount of data to download isn’t small, especially for full directories at processing level 3 and 4. It is recommended to always pick the smallest border value suitable for your research question, and to start your runs from level 5 if possible. Here is an indicative table for the total amount of data with ERA5 centerlines for all 19 RGI regions:
Level |
B 10 |
B 80 |
B 160 |
B 240 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
L0 |
979M |
979M |
979M |
979M |
L1 |
3.3G |
17G |
47G |
95G |
L2 |
8.3G |
49G |
142G |
285G |
L3 |
14G |
55G |
148G |
292G |
L4 |
58G |
152G |
296G |
|
L5 |
11G |
11G |
12G |
L4 and L5 data are not available for border 10 (the domain is too small for the downstream lines).
Certain regions are much smaller than others of course. As an indication, with prepro level 3 and a map border of 160, the Alps are ~2.1G large, Greenland ~21G, and Iceland ~660M.
Note
The data download of the preprocessed directories will occur one single time
only: after the first download, the data will be cached in OGGM’s
dl_cache_dir folder (see First step: system settings for input data).
Available pre-processed configurations#
OGGM has several configurations and directories to choose from, and the list is getting larger regularly. Don’t hesitate to ask us if you are unsure about which to use, or if you’d like to have more configurations to choose from!
To choose from a specific preprocessed configuration, use the prepro_base_url
argument in your call to workflow.init_glacier_directories(),
and set it to the url of your choice.
The recommended prepro_base_url for a standard OGGM run is:
In [1]: from oggm import DEFAULT_BASE_URL
In [2]: DEFAULT_BASE_URL
Out[2]: 'https://cluster.klima.uni-bremen.de/~oggm/gdirs/oggm_v1.6/L3-L5_files/2023.3/elev_bands/W5E5_spinup'
This is the set-up that was used to generate the OGGM 1.6.1 standard projections (OGGM global glacier projections). The basic set-up is following:
all default OGGM parameters
W5E5 reference climate
“informed three-step” mass balance model calibration (see Calibration)
Dynamic spinup with dynamic melt factor calibration
There are however multiple options to choose from. Our tutorials showcase example of applications for some of them. One can explore cluster.klima.uni-bremen.de/~oggm/gdirs/oggm_v1.6 for more options. Here follows a brief guide through the folder structure:
- Step 1:
L1_L2_files: here the directories with pre-processing level 1 and 2 can be found. L3_L5_files: here the directories with pre-processing level 3 to 5 can be found.
Step 2: one can select a version of the directories (e.g. 2023.3)
Step 3: select the flowline type, centerlines or elevation band flowlines (elev_bands), optionally with the extension of you choice in when using L1_L2_files.
Step 4: This is only needed when taking the L3_L5_files route. The folder name starts with the name of the baseline climate (e.g. w5e5) that has been used, optionally followed by one or more extensions.
Explanation of the naming convention for the folder name extensions:
_spinup indicates that the dynamic spin-up has been used for the calibration, if left out the calibration was done without the dynamic spin-up.
w_data indicates that additional data has been added to the directories: ITS-LIVE, Millan et al. ice velocity product and the consensus ice thickness estimate (all described in more detail later).
Deprecated: version 1.4 and 1.5 directories (before v1.6)
All v1.4 directories are still working with OGGM v1.6: however, you may have to change the run parameters back to their previous values. We document them here:
A. Default
If not provided with a specific prepro_base_url argument,
workflow.init_glacier_directories() will download the glacier
directories from the default urls. Here is a summary of the default configuration:
model parameters as of the
oggm/params.cfgfile at the published model versionflowline glaciers computed from the geometrical centerlines (including tributaries)
baseline climate from CRU (not available for Antarctica) using a global precipitation factor of 2.5 (path index: pcp2.5)
baseline climate quality checked and corrected if needed with
tasks.historical_climate_qc()withN=3. If the condition of at least 3 months of melt per year at the terminus and 3 months of accumulation at the glacier top is not reached, temperatures are shifted (path index: qc3).mass balance parameters calibrated with the standard OGGM procedure (path index: no_match). No calibration against geodetic MB (see options below for regional calibration).
ice volume inversion calibrated to match the ice volume from [Farinotti_etal_2019] at the RGI region level, i.e. glacier estimates might differ. If not specified otherwise, it’s also the precalibrated parameters that will be used for the dynamical run.
frontal ablation by calving (at inversion and for the dynamical runs) is switched off
To see the code that generated these directories (for example if you want to
make your own, visit cli.prepro_levels.run_prepro_levels()
or this file on github).
The urls used by OGGM per default are in the following ftp servor:
https://cluster.klima.uni-bremen.de/~oggm/gdirs/oggm_v1.4/ :
L1-L2_files/centerlines for level 1 and level 2
L3-L5_files/CRU/centerlines/qc3/pcp2.5/no_match for level 3 to 5
If you are new to this, we recommend to explore these directories to familiarize yourself to their content. Of course, when provided with an url such as above, OGGM will know where to find the respective files automatically, but is is good to understand how they are structured. The summary folder (example) contains diagnostic files which can be useful as well.
B. Option: Geometrical centerlines or elevation band flowlines
The type of flowline to use (see Glacier flowlines) can be decided at level 2 already. Therefore, the two configurations available at level 2 from these urls:
L1-L2_files/centerlines for centerlines
L1-L2_files/elev_bands for elevation bands
The default pre-processing set-ups are also available with each of these flowline types. For example with CRU:
L3-L5_files/CRU/centerlines/qc3/pcp2.5/no_match for centerlines
L3-L5_files/CRU/elev_bands/qc3/pcp2.5/no_match for elevation bands
C. Option: Baseline climate data
For the two most important default configurations (CRU or ERA5 as baseline climate), we provide all levels for both the geometrical centerlines or the elevation band flowlines:
L3-L5_files/CRU/centerlines/qc3/pcp2.5/no_match for CRU + centerlines
L3-L5_files/CRU/elev_bands/qc3/pcp2.5/no_match for CRU + elevation bands
L3-L5_files/ERA5/centerlines/qc3/pcp1.6/no_match for ERA5 + centerlines
L3-L5_files/ERA5/elev_bands/qc3/pcp1.6/no_match for ERA5 + elevation bands
Note that the globally calibrated multiplicative precipitation factor (pcp) depends on the used baseline climate (e.g. pcp is 2.5 for CRU and 1.6 for ERA5). If you want to use another baseline climate, you have to calibrate the precipitation factor yourself. Please get in touch with us in that case!
D. Option: Mass balance calibration method
There are different mass balance calibration options available in the preprocessed directories:
no_match: This is the default calibration option. For calibration, the direct glaciological WGMS data is used and the Marzeion et al., 2012 tstar method is applied to interpolate to glaciers without measurements. With this method, the geodetic estimates are not matched.
match_geod: The default calibration with direct glaciological WGMS data is still applied on the glacier per glacier level, but on the regional level the epsilon (residual) is corrected to match the geodetic estimates from Hugonnet et al., 2021. For example:
L3-L5_files/CRU/elev_bands/qc3/pcp2.5/match_geod for CRU + elevation bands flowlines + matched on regional geodetic mass balances
L3-L5_files/ERA5/elev_bands/qc3/pcp1.6/match_geod for ERA5 + elevation bands flowlines + matched on regional geodetic mass balances
match_geod_pergla: Only the per-glacier geodetic estimates from Hugonnet et al., 2021 (mean mass balance change between 2000 and 2020) are used for calibration. The mass balance model parameter \(\mu ^{*}\) of each glacier is calibrated to match individually the geodetic estimates (using
oggm.core.climate.mustar_calibration_from_geodetic_mb()). For the preprocessed glacier directories, the allowed \(\mu ^{*}\) range is set to 20–600 (more in Monthly temperature index model calibrated on geodetic MB data). This option only works for elevation band flowlines at the moment. match_geod_pergla makes only sense without “external” climate quality check and correction (i.e. qc0) as this is already done internally. For example:L3-L5_files/CRU/elev_bands/qc0/pcp2.5/match_geod_pergla for CRU + elevation bands flowlines + matched geodetic mass balances on individual glacier level
L3-L5_files/ERA5/elev_bands/qc0/pcp1.6/match_geod_pergla for ERA5 + elevation bands flowlines + matched geodetic mass balances on individual glacier level
Warning
make sure that you use the oggm_v1.6 directory for match_geod_pergla and match_geod_pergla_massredis! In the gdirs/oggm_v1.4 folder from the OGGM server, the match_geod_pergla preprocessed directories have a minor bug in the calibration (see this GitHUB issue). This bug is removed in the latest OGGM version and the corrected preprocessed glacier directories are inside the gdirs/oggm_v1.6 folder.
E. Further set-ups
Here is a list of other available configurations at the time of writing (explore the server for more!):
L3-L5_files/CERA+ERA5/elev_bands/qc3/pcp1.6/no_match for CERA+ERA5 + elevation bands flowlines
L3-L5_files/CERA+ERA5/elev_bands/qc3/pcp1.6/match_geod for CERA+ERA5 + elevation bands flowlines + matched on regional geodetic mass balances
L3-L5_files/ERA5/elev_bands/qc3/pcp1.8/match_geod for ERA5 + elevation bands flowlines + matched on regional geodetic mass balances + precipitation factor 1.8
L3-L5_files/CRU/elev_bands/qc0/pcp2.5/match_geod for CRU + elevation bands flowlines + matched on regional geodetic mass balances + no climate quality check
L3-L5_files/CRU/elev_bands/qc0/pcp2.5/no_match for CRU + elevation bands flowlines + no climate quality check
L3-L5_files/CRU/elev_bands/qc0/pcp2.5/match_geod_pergla_massredis for CRU + elevation bands flowlines + matched on regional geodetic mass balances + mass redistribution instead of SIA (see: Mass redistribution curve model)
L3-L5_files/ERA5/elev_bands/qc0/pcp1.6/match_geod_pergla_massredis for ERA5 + elevation bands flowlines + matched on regional geodetic mass balances + mass redistribution instead of SIA
Note: the additional set-ups might not always have all map sizes available. Please
get in touch if you have interest in a specific set-up. Remember that per default, the climate quality check
and correction (oggm.tasks.historical_climate_qc()) is applied (qc3). However, if the pre-processed directory
has the path index “qc0”, it was not applied (except for match_geod_pergla where it is applied internally).
F. Error analysis and further volume and mass change comparison for different pre-processed glacier directories
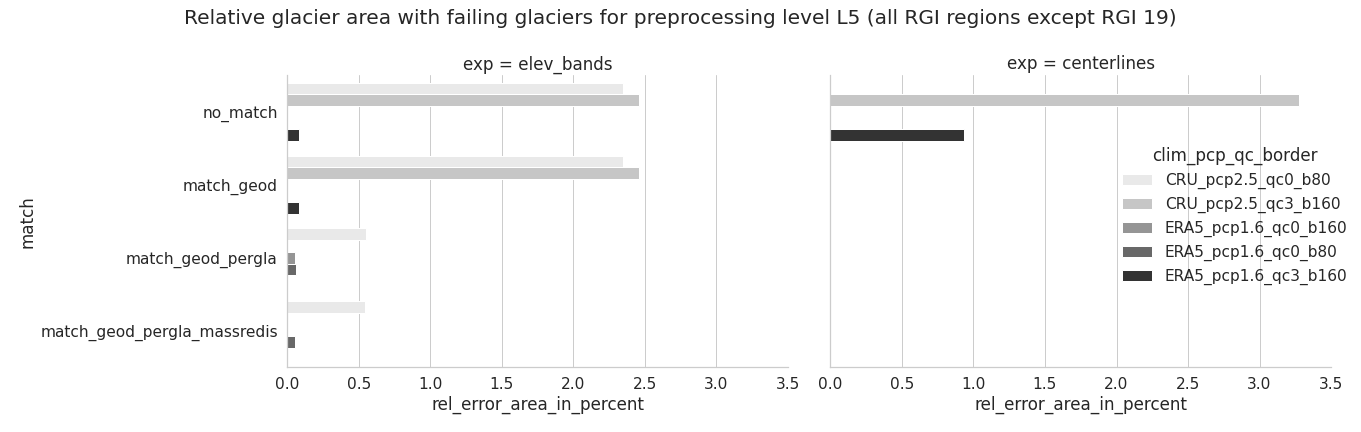
Overall, calibrating with ERA5 using a precipitation factor of 1.6 results in much less errors than CRU with pf=2.5. In addition, less errors occur for elevation bands and when using the match_geod_pergla option.#
A more detailed analysis about the type, amount and relative failing glacier area (in total and per RGI region) can be found in this error analysis jupyter notebook.
If you are also interested in how the “common” non-failing glaciers differ in terms of historical volume change, total mass change and specific mass balance between different pre-processed glacier directories, you can check out this jupyter notebook.
Additional available data#
Here follows a description of the additional data that can be added to the pre-processed glacier directories, by choosing the ‘w_data’ option.
ITS_LIVE#
The ITS_LIVE ice velocity products can be downloaded and reprojected to the glacier directory (visit our tutorials if you are interested!).
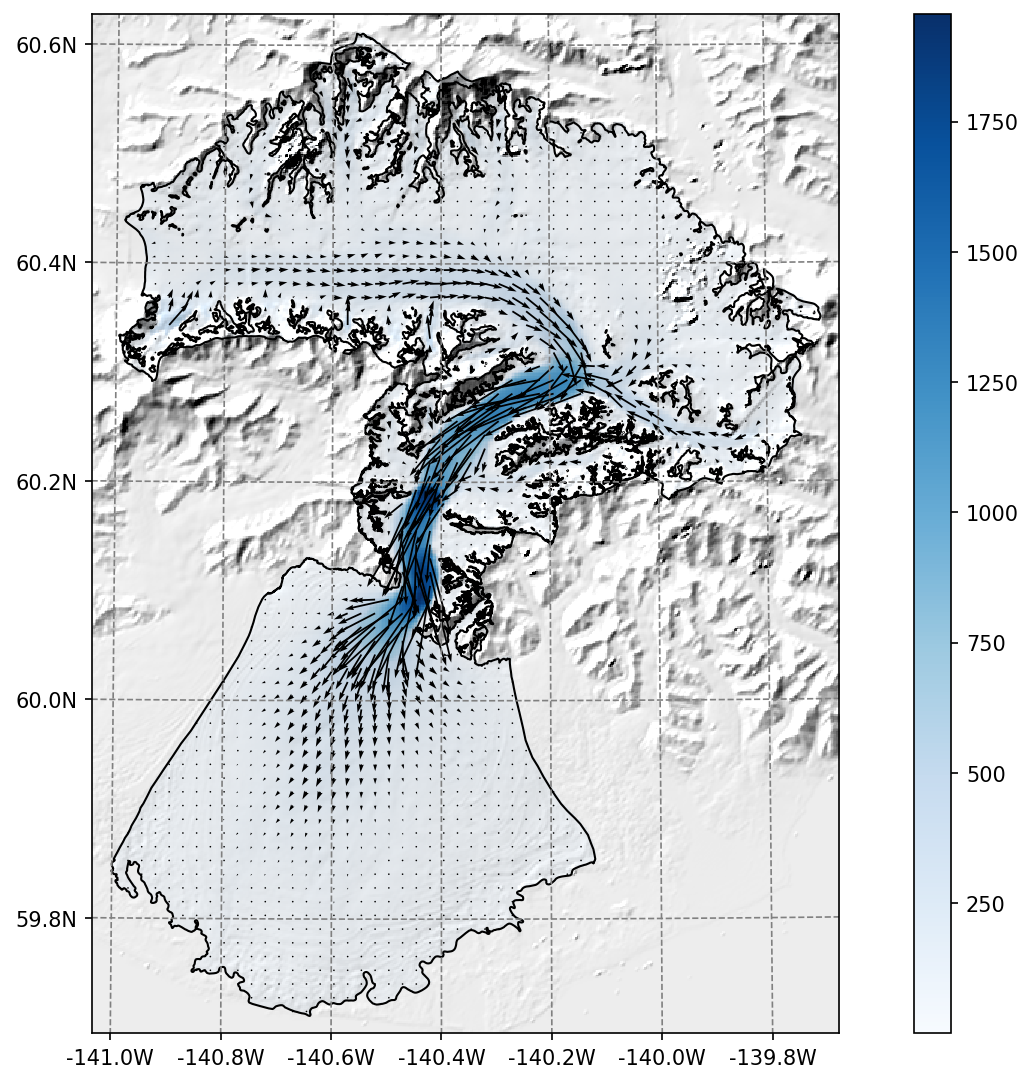
Example of the reprojected ITS_LIVE products at Malaspina glacier#
The data source used is https://its-live.jpl.nasa.gov/#data Currently the only data downloaded is the 120m composite for both (u, v) and their uncertainty. The composite is computed from the 1985 to 2018 average.
If you want more velocity products, feel free to open a new topic on the OGGM issue tracker!
Ice thickness#
The Farinotti et al., 2019 ice thickness products can be downloaded and reprojected to the glacier directory (visit our tutorials if you are interested!).
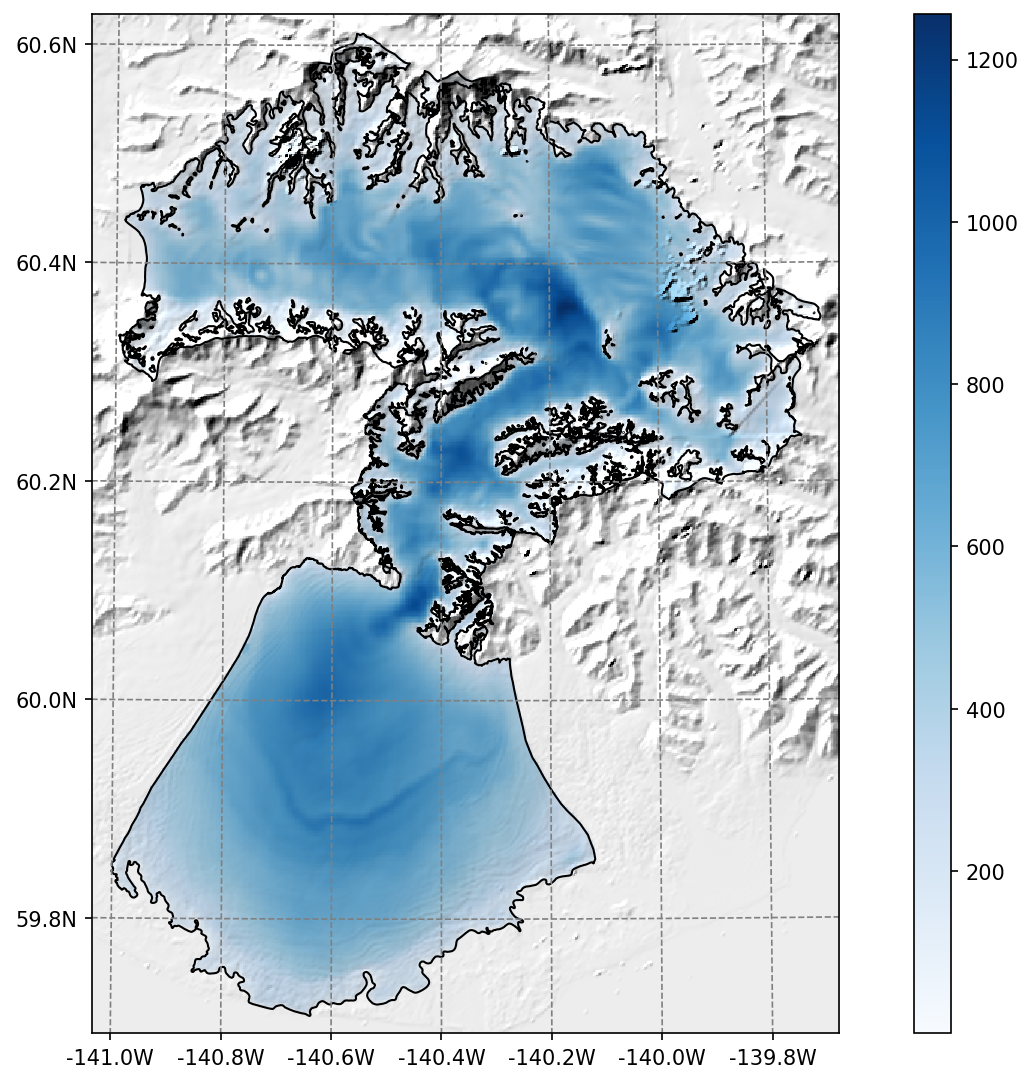
Example of the reprojected ice thickness products at Malaspina glacier#
Millan et al. (2022) ice velocity and thickness products#
Similarly, we provide data from the recent Millan et al. (2022) global study (visit our tutorials if you are interested!).
Raw data sources#
If you want to run your own workflow from A to Z, or if you would like to know which data are used in OGGM before being available in the pre-processed directories, read further for some more details!
Glacier outlines and intersects#
Glacier outlines are obtained from the Randolph Glacier Inventory (RGI). We recommend to download them right away by opening a python interpreter and type:
from oggm import cfg, utils
cfg.initialize()
utils.get_rgi_intersects_dir()
utils.get_rgi_dir()
The RGI folders should now contain the glacier outlines in the shapefile format, a format widely used in GIS applications. These files can be read by several software (e.g. qgis), and OGGM can read them too.
The “RGI Intersects” shapefiles contain the locations of the ice divides (intersections between neighboring glaciers). OGGM can make use of them to determine which bed shape should be used (rectangular or parabolic). See the rgi tools documentation for more information about the intersects.
The following table summarizes the RGI attributes used by OGGM. It can be useful to refer to this list if you use your own glacier outlines with OGGM.
RGI attribute |
Equivalent OGGM variable |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
RGIId |
|
|
GLIMSId |
|
not used |
CenLon |
|
|
CenLat |
|
|
O1Region |
|
not used |
O2Region |
|
not used |
Name |
|
used for graphics only |
BgnDate |
|
|
Form |
|
|
TermType |
|
|
Status |
|
|
Area |
|
|
Zmin |
|
recomputed by OGGM |
Zmax |
|
recomputed by OGGM |
Zmed |
|
recomputed by OGGM |
Slope |
|
recomputed by OGGM |
Aspect |
|
recomputed by OGGM |
Lmax |
|
recomputed by OGGM |
Connect |
not included |
|
Surging |
not included |
|
Linkages |
not included |
|
EndDate |
not included |
For Greenland and Antarctica peripheral glaciers, OGGM does not take into account the
connectivity level between the Glaciers and the Ice sheets.
We recommend to the users to think about this before they
run the task: workflow.init_glacier_directories.
Comments
- 1
The RGI id needs to be unique for each entity. It should resemble the RGI, but can have longer ids. Here are example of valid IDs:
RGI60-11.00897,RGI60-11.00897a,RGI60-11.00897_d01.- 2(1,2)
CenLonandCenLatare used to center the glacier local map and DEM.- 3
The date is the acquisition year, stored as an integer.
- 4
Glacier type:
'Glacier','Ice cap','Perennial snowfield','Seasonal snowfield','Not assigned'. Ice caps are treated differently than glaciers in OGGM: we force use a single flowline instead of multiple ones.- 5
Terminus type:
'Land-terminating','Marine-terminating','Lake-terminating','Dry calving','Regenerated','Shelf-terminating','Not assigned'. Marine and Lake terminating are classified as “tidewater” in OGGM and cannot advance - they “calve” instead, using a very simple parameterization.- 6
Glacier status:
'Glacier or ice cap','Glacier complex','Nominal glacier','Not assigned'. Nominal glaciers fail at the “Glacier Mask” processing step in OGGM.- 7
The area of OGGM’s flowline glaciers is corrected to the one provided by the RGI, for area conservation and inter-comparison reasons. If you do not want to use the RGI area but the one computed from the shape geometry in the local OGGM map projection instead, set
cfg.PARAMS['use_rgi_area']toFalse. This is useful when using homemade inventories.
Topography data#
When creating a Glacier directories, a suitable topographical data source is chosen automatically, depending on the glacier’s location. OGGM supports a large number of datasets (almost all of the freely available ones, we hope). They are listed on the RGI-TOPO website.
The current default is to use the following datasets:
NASADEM: 60°S-60°N
COPDEM90: Global, with missing regions (islands, etc.)
GIMP, REMA: Regional datasets
TANDEM: Global, with artefacts / missing data
MAPZEN: Global, when all other things failed
These data are chosen in the provided order. If a dataset is not available, the next on the list will be tested: if the tested dataset covers 75% of the glacier area, it is selected. In practice, NASADEM and COPDEM90 are sufficient for all but about 300 of the world’s glaciers.
These data are downloaded only when needed (i.e. during an OGGM run)
and they are stored in the dl_cache_dir
directory. The gridded topography is then reprojected and resampled to the local
glacier map. The local grid is defined on a Transverse Mercator projection centered over
the glacier, and has a spatial resolution depending on the glacier size. The
default in OGGM is to use the following rule:
where \(\Delta x\) is the grid spatial resolution (in m), \(S\) the glacier area (in km\(^{2}\)) and \(d_1\), \(d_2\) some parameters (set to 14 and 10, respectively). If the chosen spatial resolution is larger than 200 m (\(S \ge\) 185 km\(^{2}\)) we clip it to this value.
Important: when using these data sources for your OGGM runs, please refer
to the original data provider of the data! OGGM adds a dem_source.txt
file in each glacier directory specifying how to cite these data. We
reproduce this information
here.
Warning
A number of glaciers will still suffer from poor topographic information. Either the errors are large or obvious (in which case the model won’t run), or they are left unnoticed. The importance of reliable topographic data for global glacier modelling cannot be emphasized enough, and it is a pity that no consistent, global DEM is yet available for scientific use. Visit rgitools for a discussion about our current efforts to find “the best” DEMs.
Note
In this blogpost we talk about which requirements a DEM must fulfill to be helpful to OGGM. And we also explain why and how we preprocess some DEMs before we make them available to the OGGM workflow.
